To address the rapid consumption of protective windows in laser welding applications (especially with handheld laser welding machines), here are targeted solutions:
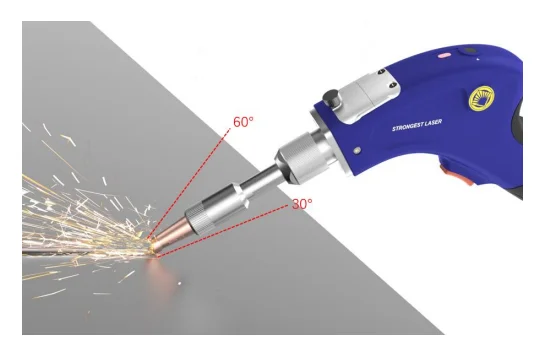
1. Angle of holding the torch
Keep the angle between the gun barrel and the surface of the workpiece within the range of 30°~60°. This angle can effectively protect the lens and reduce contamination inside the device by changing the trajectory of the sparks,using gravity and aerodynamic effects to divert most of the sparks away from the inlet direction of the protective window.
2. Adjust the air pressure and airflow
- Air flow>15L/min
- Air pressure 0.15Mpa~0.3Mpa/min
3. Protective molten pool:
- Inert gases (such as argon, helium) or mixed gases are used to isolate the air and the metal molten pool.
- Blowing off sparks: The airflow blows away the metal sparks generated during the welding process, reducing its adhesion to the surface of the protective window.
- Cooling and stabilizing the beam: The coaxial airflow (coaxial with the laser beam) can cool the protective window and prevent the window from being damaged by high temperatures.
4. keep the window surface free
Contamination of the window can lead to a sharp increase in the problem of protecting the window, damaging the protective window and failing to achieve the welding effect.
5. Power ramp up
The power needs to be changed to a gentle rise adjustment to reduce the sudden temperature change on the surface of the workpiece to reduce sparks.
6. The surface of the material is oily and rusty
Under laser irradiation, the loose rust layer (including Fe₃O₄, etc.) may partially peel off or melt, forming iron oxide particles that are sprayed onto the surface of the protective window with protecitve gas or melt pool sparks.
Grease decomposes at high temperatures into hydrocarbon gases like CO, H2, etc., which can form bubbles in the molten pool, which cause sparks when the bubbles burst. Especially when the oil layer is thicker, the amount of gas produced by decomposition is greater, and the bubbles are more unstable.














