Laser welding machines are the backbone of modern high-precision manufacturing, offering unmatched efficiency, minimal thermal distortion, and exceptional weld quality. But behind every flawless laser weld lies a meticulously engineered structure. Here, we break down the core components, auxiliary systems, and key design features that define the structural design of a laser welding machine.
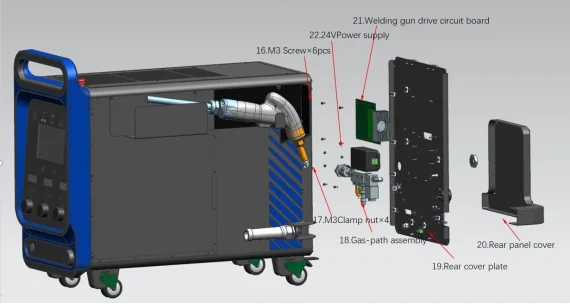
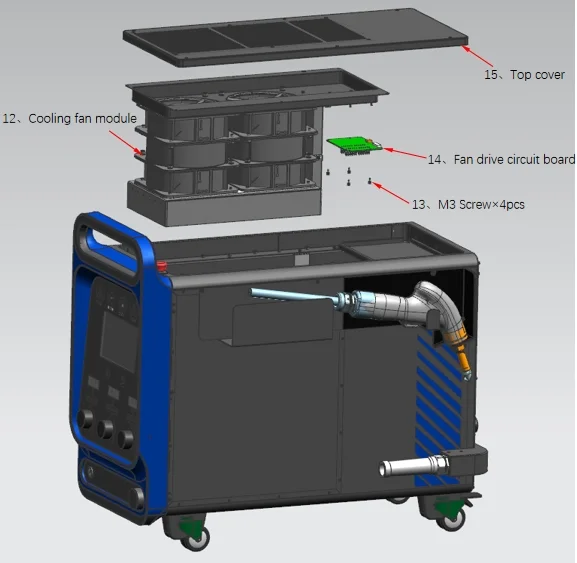
Core Components of a Laser Welding Machine
Laser Welding Host Unit
Laser Generator: The heart of the welding machine, responsible for producing a high-energy-density laser beam for precise and powerful welding.
Optical Path System: Includes focusing lenses, mirrors, and other optical elements that guide and focus the beam onto the workpiece.
Power Supply & Control System: Regulates laser power, beam position, and welding speed for consistent, high-quality welds.
Cooling System: Uses an industrial water chiller to prevent overheating of the laser generator; higher laser power requires greater cooling capacity.
Automated Workbench or Motion System
Enables laser beam movement along programmed paths for automated welding.
Configurations include stationary laser head with moving workpiece, moving laser head with stationary workpiece, or both moving.
CNC programming allows precise, repeatable welding cycles.
Workholding Fixtures
Secure and position workpieces accurately for automated production.
Fixture design directly impacts productivity and product yield in mass production.
Observation System
Integrated microscope or CCD camera enables real-time monitoring and quality inspection during welding.
Auxiliary Components

Additional Laser Components: May include single or dual-pulse xenon lamps for initial light wave generation.
Gas System: Supplies shielding gases (e.g., argon, helium) to prevent oxidation and ensure clean welds.
Electrical Control System: Includes power switches, LCD panels, and motion control units for precise process management.
Key Structural Design Features
High Integration: Compact design combines multiple subsystems to save space and improve usability.
Precision Control: Advanced optics and electronics allow for micron-level beam placement.
Flexibility: Adjustable worktables and fixtures adapt to various part geometries and sizes.
Energy Efficiency: Minimal heat-affected zone (HAZ) and low energy loss make laser welding both fast and cost-effective.
The structural design of a laser welding machine is a complex, highly integrated engineering system, where each component works in harmony to deliver exceptional weld precision, speed, and reliability. Whether for automotive, aerospace, electronics, or medical device manufacturing, mastering the design and integration of these systems is key to achieving peak welding performance.
For more in-depth technical insights and customized laser welding solutions, visit STRION LASER Official Website.