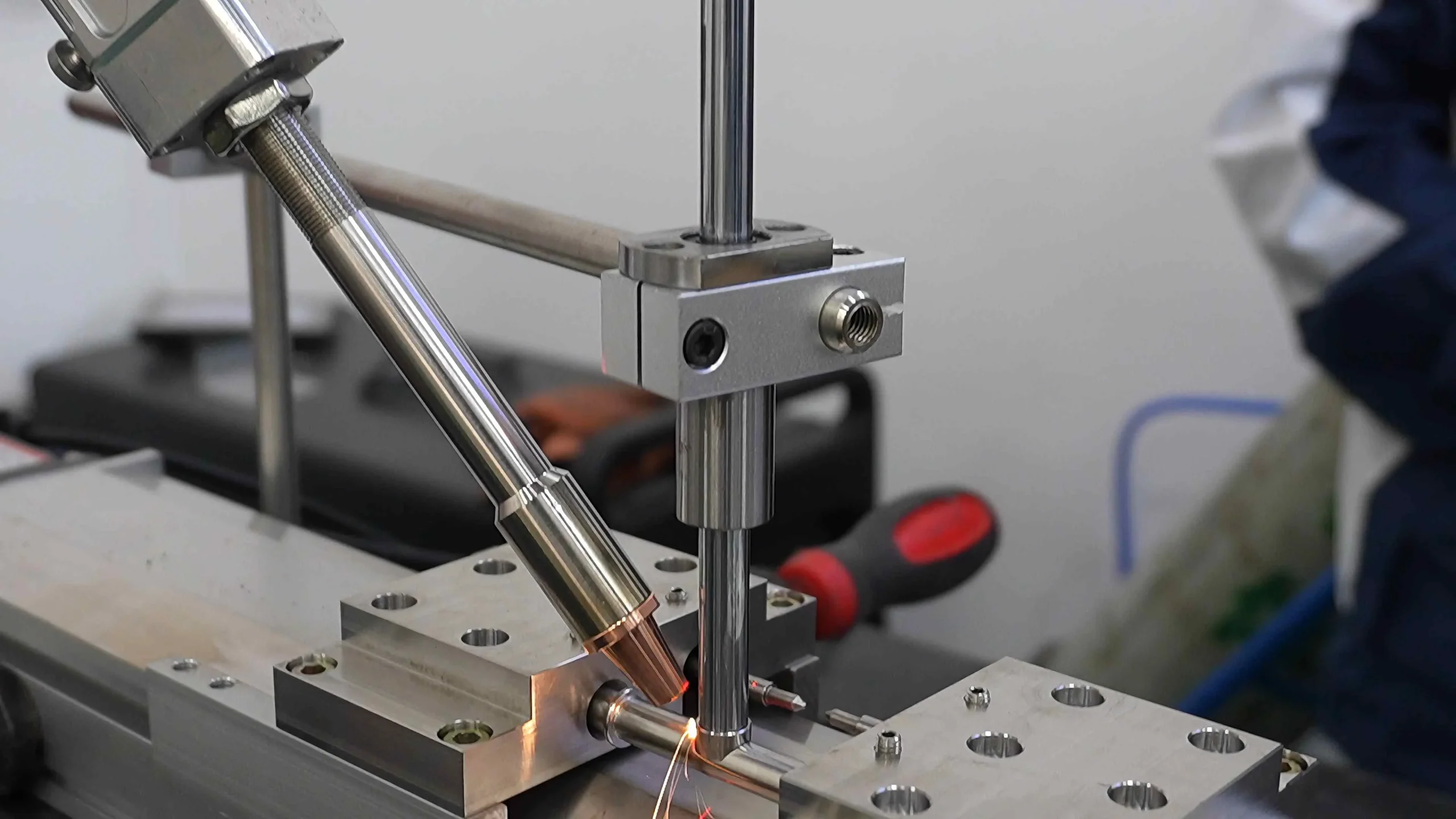
Empowering intelligent manufacturing with advanced laser welding solutions
STRION LASER recently completed a successful application case of automated robotic laser welding for saddle-port thin tubes — a process requiring exceptional precision and thermal control. This case highlights the strengths of STRION’s automated laser welding systems in handling complex, thin-walled components for industries demanding high accuracy.

Project Overview
Industry: Automotive sensor housing
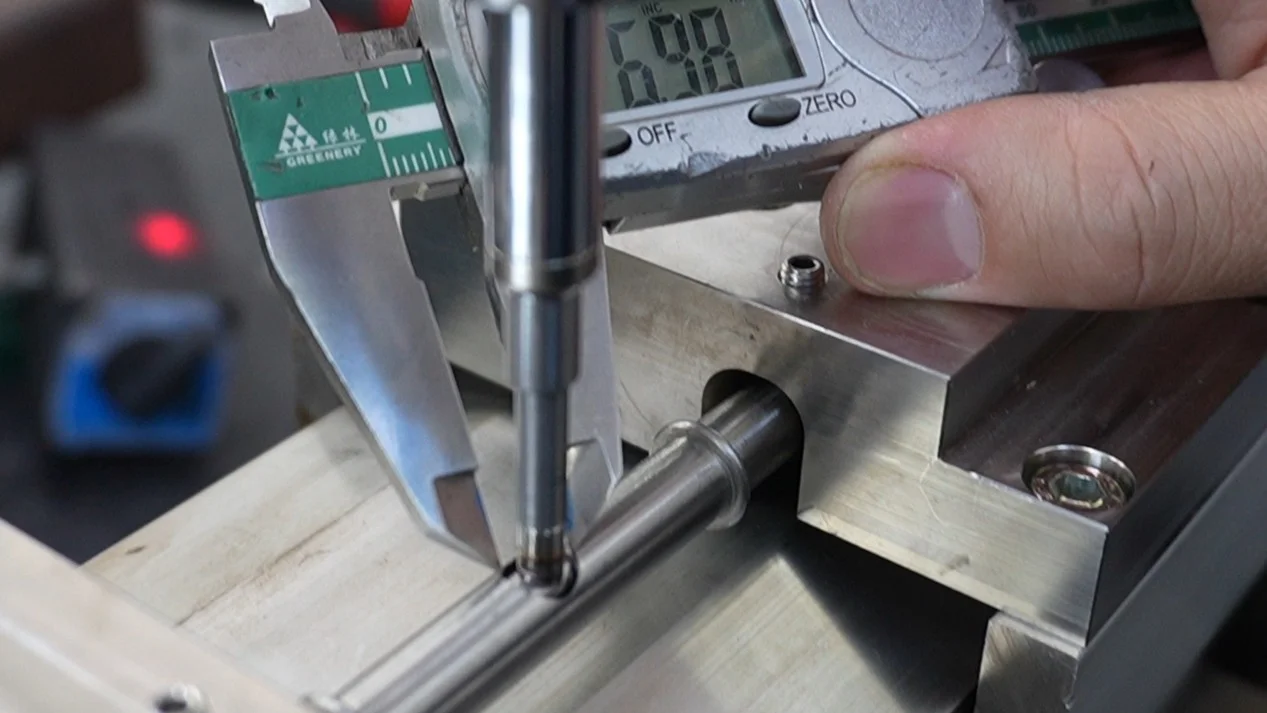
Inner diameter: 4.35 mm
Outer diameter: 7.00 mm
Weld width: 3.63 mm
Given the small scale and tight tolerances, the project posed a complex technical challenge—one that STRION’s automated laser welding platform handled with precision and stability.

Why Automated Laser Welding?
Compared to traditional welding methods, automated laser welding offers key advantages:
Extremely fine laser spot, enabling concentrated energy delivery
High penetration capability with minimal heat input
Smaller heat-affected zone (HAZ), essential for maintaining thin tube integrity
These benefits make laser welding ideal for high-precision fabrication, especially when welding thin tubes where deformation and burn-through are common challenges.
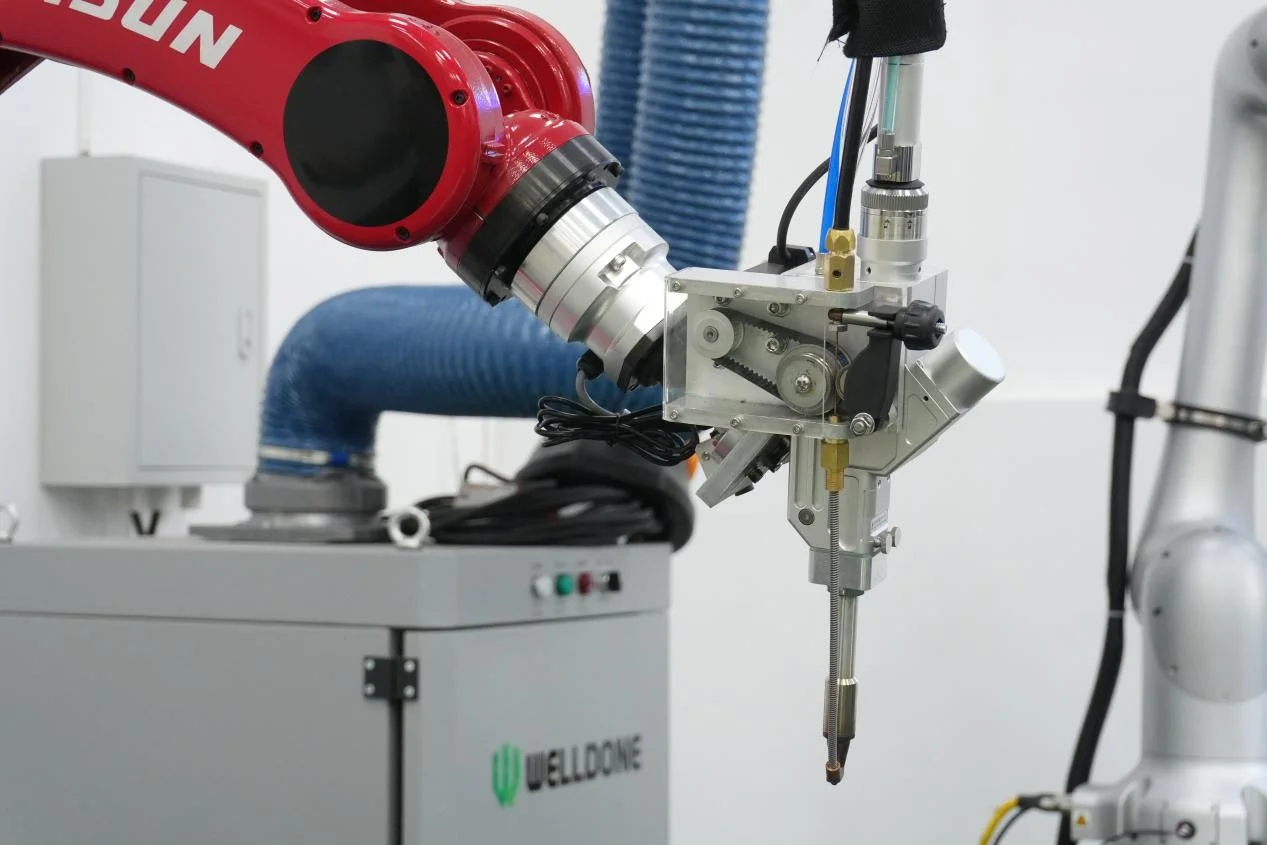

Pre-Weld Preparation
To ensure stable and high-quality results, the following measures were taken:
Surface cleaning: All parts were thoroughly cleaned to remove oil, rust, and surface contaminants, preventing spatter and ensuring consistent arc behavior.
Controlled welding speed: A balanced speed was maintained—too fast could result in lack of fusion; too slow risks burn-through on thin materials.

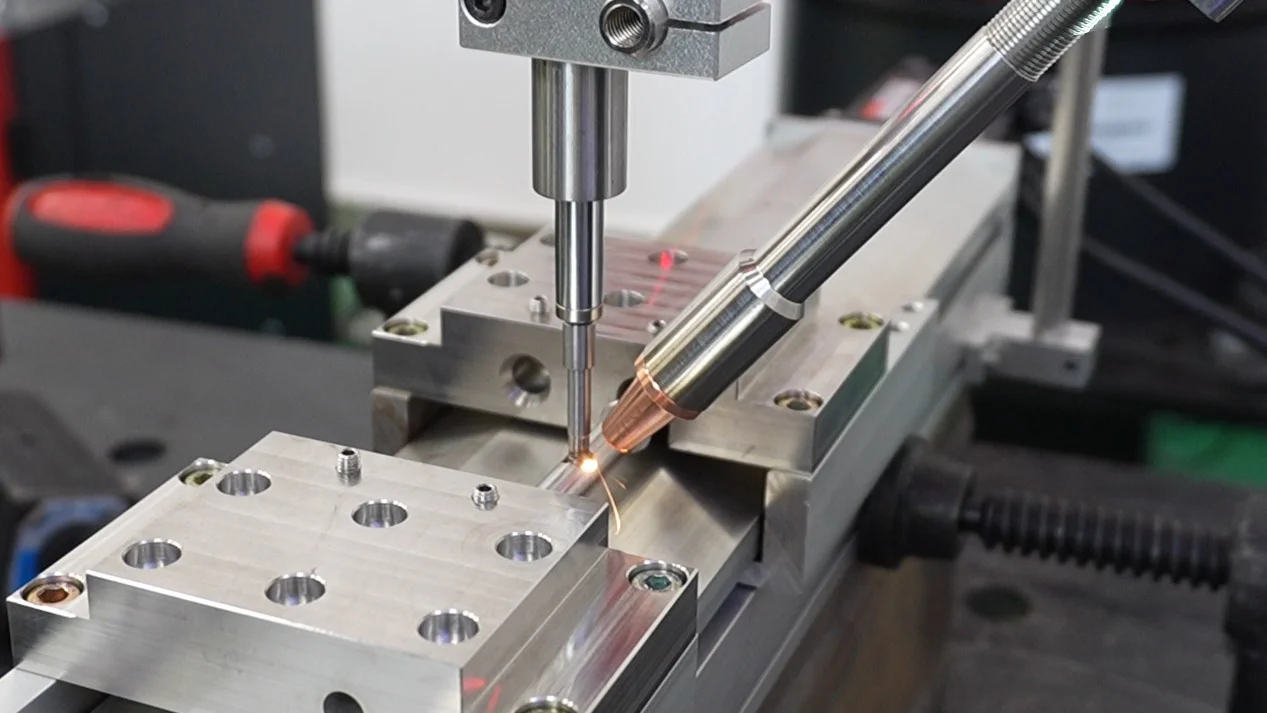
Welding Process Best Practices
STRION’s engineering team applied the following techniques to further enhance weld quality and dimensional control:
Tack welding: Initial tack welds were applied to hold the part in place and prevent shifting or deformation during the main weld.
Segmented welding: When deformation sensitivity was high, segmented welding was used to reduce thermal buildup.
Backside shielding: In applications with high oxidation risk, backside gas protection was introduced to maintain weld cleanliness.
Precision fixturing: Custom jigs and clamps were used to hold the workpiece steady and minimize warping.

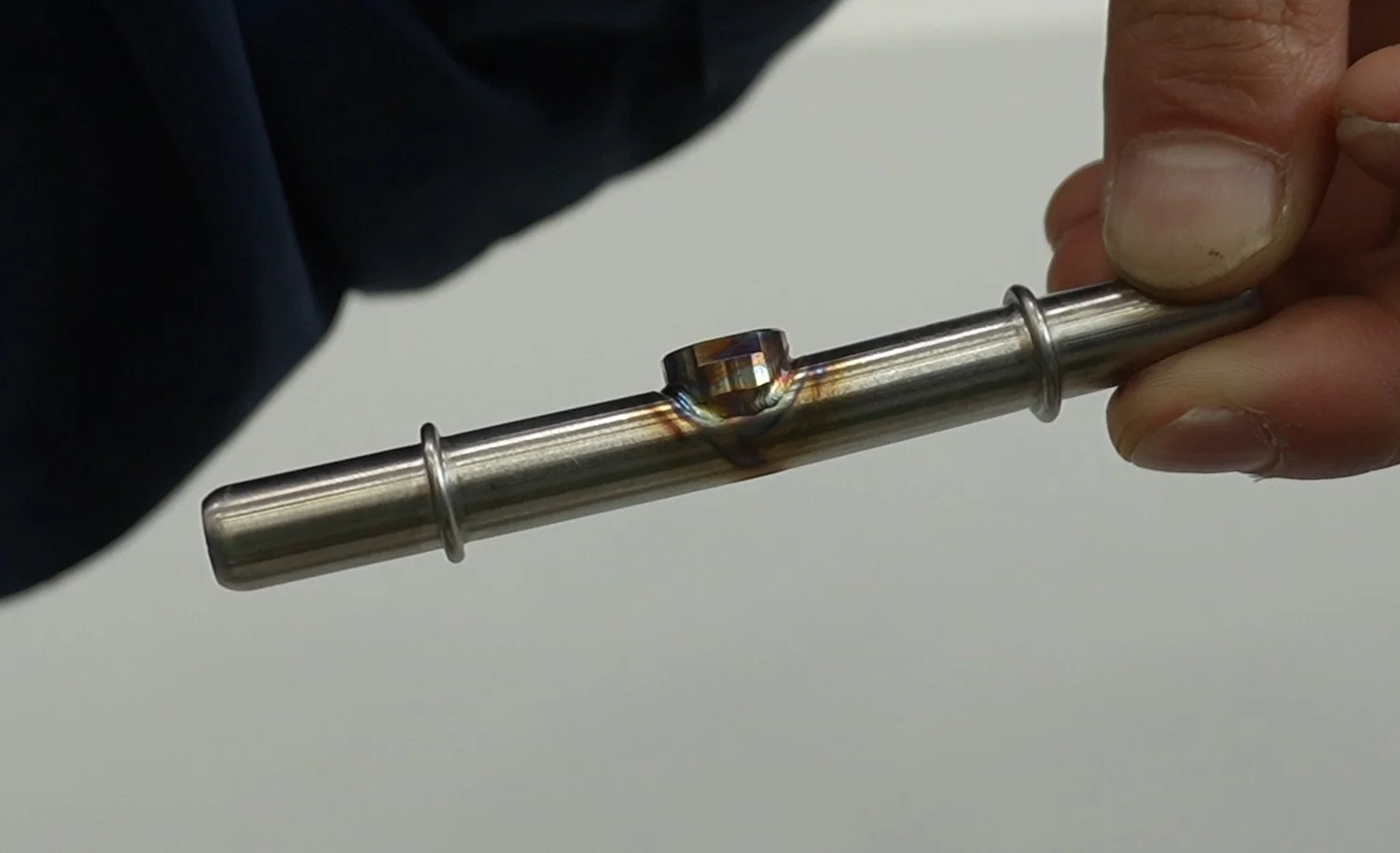
Welding thin-walled components—especially in small-diameter configurations—requires a precise balance of technique, equipment, and process control. STRION LASER’s automated robotic welding solution provides consistent, high-quality results while minimizing operator dependence and production variability.
By continuing to push the boundaries of precision laser technology, STRION LASER empowers manufacturers with efficient, scalable, and industry-specific solutions for modern production challenges.