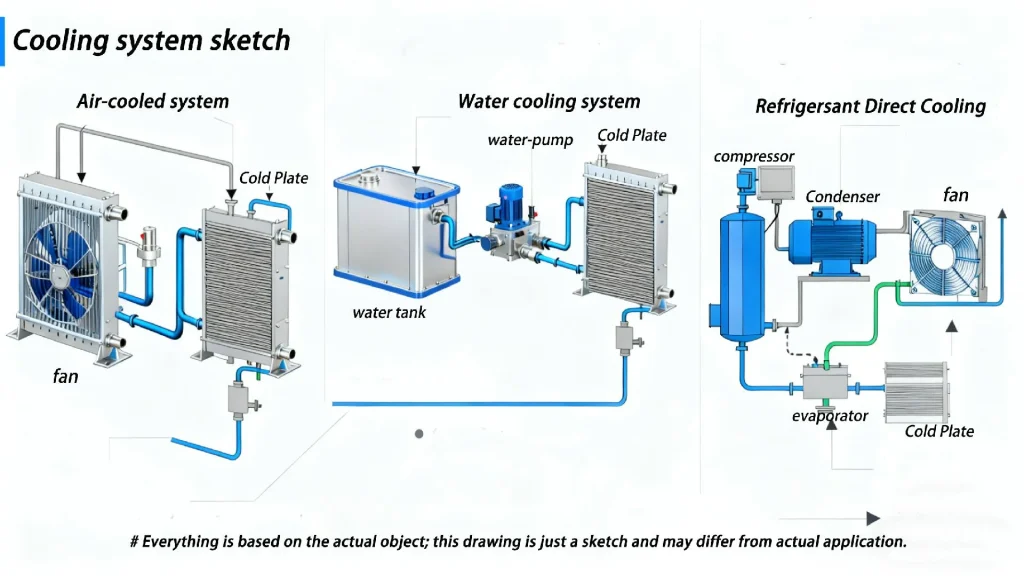
Handheld Laser Welder Cooling Systems Explained
Air Cooling vs Water Cooling vs Dual-Circuit Refrigerant Direct Cooling
In any handheld laser welding machine, the cooling system plays a decisive role in maintaining consistent performance and welding quality.
As laser power increases and working environments become more demanding, temperature management directly impacts stability, efficiency, and equipment lifespan.
Today, the three most common cooling methods are air cooling, water cooling, and the advanced dual-circuit refrigerant direct cooling system.
Let’s explore how they differ and which one fits modern industrial needs best.
1. Air Cooling: Simple Design, Limited by Ambient Temperature
Air cooling is the most basic type of heat dissipation system. It uses fans to circulate air through the device, removing heat from internal components.
Its structure is compact and cost-effective, but performance is highly dependent on environmental conditions.
Key Features:
- Advantages: Low cost, simple design, no coolant required.
- Disadvantages: Limited cooling capacity; performance drops sharply in hot or cold environments.
- Working Range: Typically operates within 25°C–30°C.
- Runtime: Continuous operation may lead to overheating or startup failure.
Best For:
Short-term, light-duty welding tasks where temperature fluctuation is minimal.
2. Water Cooling: Reliable but Maintenance-Heavy
Water cooling remains the most widely used cooling method in today’s laser welding machines.
It uses circulating coolant to transfer heat from the laser source to a condenser or chiller unit.
Key Features:
- Advantages: Efficient heat dissipation with steady temperature control.
- Disadvantages: Operating temperature range limited to 5°C–50°C;Requires periodic coolant replacement and antifreeze additives in winter;Risk of scaling, clogging, or leakage over time.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning and monitoring are essential to ensure consistent cooling performance.
Best For:
Workshops and factories operating in stable room-temperature environments.
3. Dual-Circuit Refrigerant Direct Cooling: Intelligent and Energy-Efficient
The dual-circuit refrigerant direct cooling system represents a major breakthrough in handheld laser welder temperature control.
By using two independent circulation loops — one for the laser core (pump source and optics) and another for intelligent system temperature balancing — it achieves real-time thermal precision and maintenance-free stability.
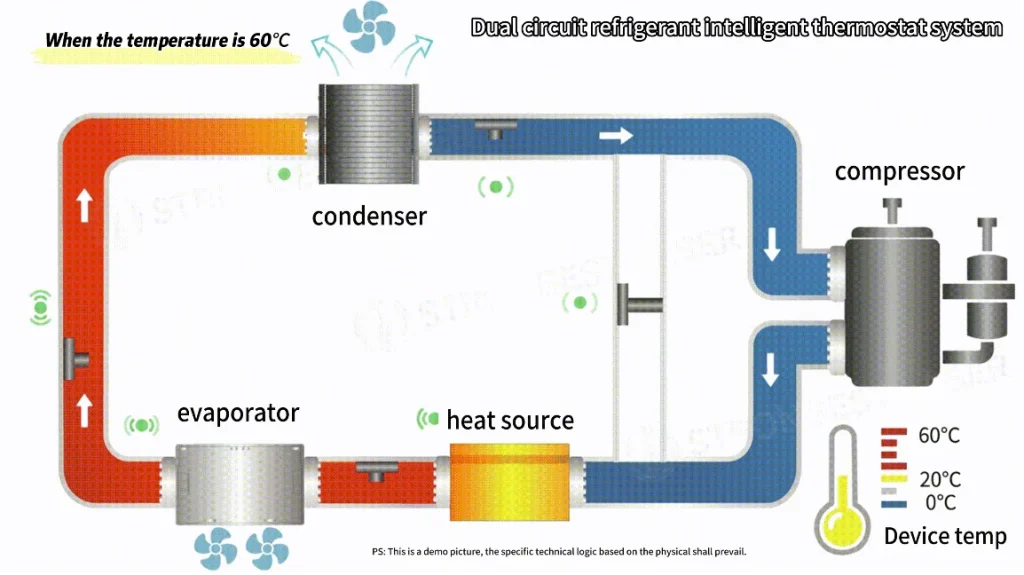
This innovation directly enables two key technological upgrades that air- and water-cooled systems cannot achieve:
① Support for 14 μm Small-Core Fiber Technology
Stable temperature management makes it possible to adopt 14 μm small-core fiber technology.
Compared with conventional 25 μm–50 μm fibers used in air- or water-cooled welders, this smaller core dramatically improves laser beam density and energy concentration, resulting in:
- Tighter and cleaner weld seams,
- Greater penetration and reduced spatter,
- Higher precision in thin metal welding applications.
Air- and water-cooling systems struggle to maintain the precise thermal balance required for such small-core fibers, often leading to beam instability and optical damage during long-term operation.
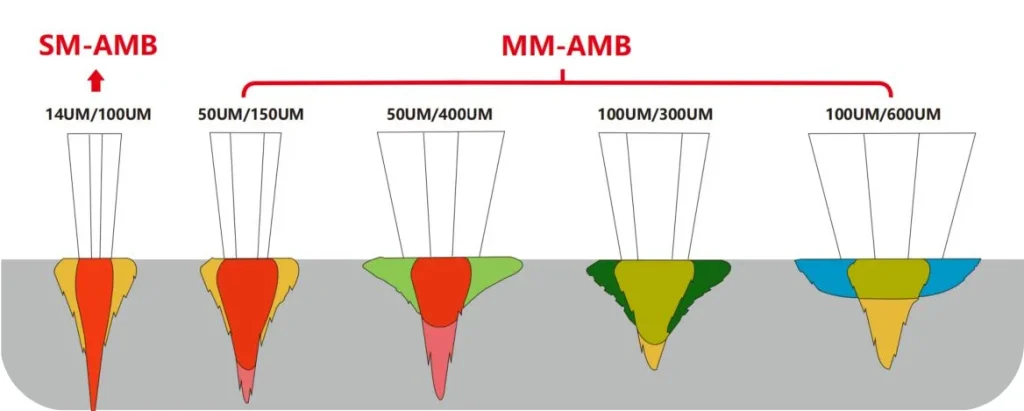
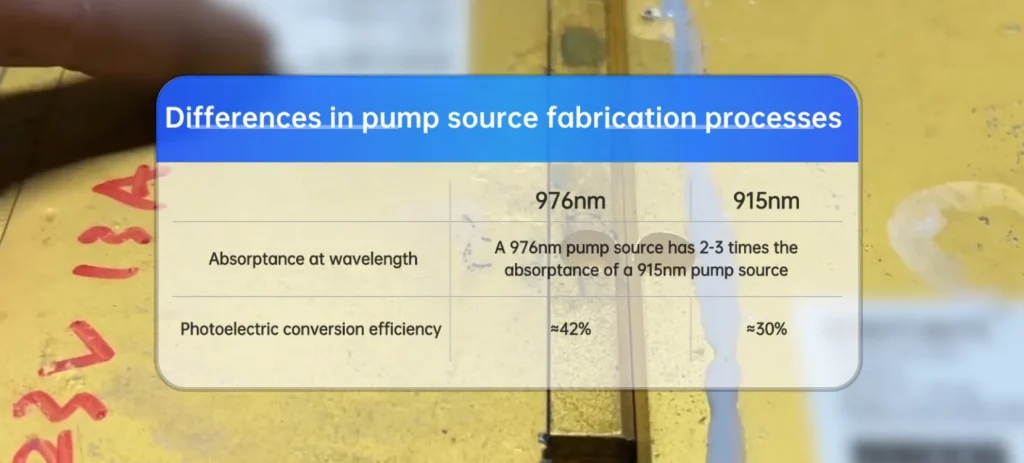
② Equipped with 976 nm Pump Source for Peak Efficiency
The system integrates a 976 nm pump source, which achieves higher photoelectric conversion efficiency compared with traditional 915 nm sources used in conventional welders.
Thanks to precise thermal regulation provided by the refrigerant system, the 976 nm pump maintains optimal working temperature and consistent laser output, even under heavy load.
Performance Benefits:
- Up to 10–15% higher energy efficiency,
- Significantly improved beam stability,
- Longer pump lifespan due to reduced thermal stress.
Neither air nor water cooling can offer this level of stability; fluctuations in coolant temperature or ambient heat often cause power drift and reduced conversion efficiency.
Best For:
High-power, long-duration industrial welding applications or environments with extreme temperature conditions.
4. System Comparison Overview
| Feature | Air Cooling | Water Cooling | Dual-Circuit Refrigerant Cooling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | Air convection | Liquid circulation | Direct refrigerant heat transfer |
| Temperature Range | 25–30 °C | 5–50 °C | -30 °C to 60 °C (constant) |
| Temperature Control | Passive | Semi-stable | Intelligent & Precise |
| Energy Efficiency | Average | Moderate | Up to 50% higher |
| Compatible Core Fiber | ≥25 μm | ≥25 μm | ≥14 μm |
| Pump Source | 915 nm | 915 nm | 976 nm (High Conversion) |
| Maintenance | Low | High (coolant change) | None (sealed loop) |
| Welding Stability | Limited | Moderate | Superior – <1% Power Fluctuation |
| Suitable For | Light tasks | General industry | High-precision, long-duty welding |
5. Selecting the Right Cooling System for Stable Welding
The choice of cooling system determines how reliably a laser welder performs over time.
From the comparison above:
Air Cooling offers simplicity but struggles under extended workloads.
Water Cooling provides stable temperature control yet requires frequent maintenance.
Dual-Circuit Refrigerant Direct Cooling combines precision, efficiency, and long-term stability, making it ideal for modern production environments.
For manufacturers or workshops running high-power, continuous welding, refrigerant direct cooling systems provide consistent temperature regulation, uniform weld seams, and reduced downtime—all while extending equipment lifespan.
6. The Future of Laser Welder Cooling Technology
As laser welding continues moving toward higher power and greater precision, traditional air- and water-cooling methods are reaching their limits.
Dual-circuit refrigerant direct cooling stands out as the next-generation solution—offering intelligent temperature control, superior efficiency, and reliable performance in any environment.
This system ensures that handheld laser welders maintain optimal output stability under 24/7 industrial workloads, marking a new standard for precision welding technology.
Looking for a more stable and energy-efficient laser welding solution?
Contact our team to learn more about our dual-circuit refrigerant direct cooling technology and find the right handheld laser welder for your needs.