Laser welding technology has transformed manufacturing, offering precision and efficiency previously unattainable with traditional welding methods. Among the advances, handheld laser welding machines have emerged as a versatile tool, valued for their portability, ease of use, and precise weld quality. These compact yet powerful devices allow for intricate, high-quality welding tasks that can be performed quickly and accurately across various industries. This article explores the operation, advantages, and applications of handheld laser welding machines, detailing how they enhance productivity in diverse industrial settings.
Working Principle of Handheld Laser Welding Machines
Handheld laser welding machines function by focusing a high-energy laser beam on the welding surface, melting the metal and forming a solid bond upon cooling. This method contrasts with traditional arc welding, as it delivers concentrated energy with minimal heat dispersion, reducing distortion and enhancing weld precision. Typically, handheld laser welders utilize fiber lasers or diode lasers due to their reliability and efficiency. A fiber laser, for example, channels laser light through fiber optics to the workpiece, allowing for a consistent, targeted weld with minimal heat-affected zones.
With basic controls and ergonomic design, handheld laser welders allow technicians to manage precise welds even in confined spaces or on complex parts, making them especially valuable for intricate or on-site welding tasks.
Advantages of Handheld Laser Welding Machines in Industrial Settings
Handheld laser welding machines bring a suite of benefits that streamline production processes and improve overall efficiency:
High Speed and Productivity: Compared to traditional methods, laser welding is considerably faster, reducing production time and enabling higher throughput.
Quality and Precision: The concentrated laser beam creates smooth, consistent welds with minimal spatter and oxidation, ensuring high-quality joints.
Reduced Heat Input and Minimal Distortion: With focused energy, less heat is transferred to surrounding areas, which preserves material integrity and reduces the risk of warping.
Flexibility and Accessibility: The handheld design is ideal for hard-to-reach areas or on-site repairs, and the machines can weld a wide variety of metals and alloys.
Ease of Operation and Training: With simple controls, handheld laser welders are user-friendly, allowing technicians to achieve proficiency quickly, which lowers the overall training costs.
Primary Industrial Applications
Handheld laser welders have found applications across numerous industries where precision and durability are essential:
Automotive Industry: In automotive manufacturing, laser welding is vital for producing body panels, frames, and battery enclosures for electric vehicles. The precision of handheld laser welders ensures high-strength, low-distortion joints, ideal for vehicle prototypes and lightweight components.

Electronics Industry: Miniature welding of connectors, smartphone components, and circuit boards is enabled by laser welders’ ability to perform micro-welding. This capability is critical in electronics, where precision is crucial to avoid damaging small, delicate parts.
Aerospace Industry: The aerospace industry demands lightweight yet strong components. Handheld laser welding provides precision welding for components made from specialized alloys, such as titanium and aluminum, often found in aircraft frames and engine components.
Metal Fabrication and Construction: Metal fabrication benefits from handheld laser welders for custom metalwork, structural components, and on-site repairs. The portability of handheld devices allows for versatile fabrication, accommodating tasks like repairing heavy equipment or assembling metal structures.
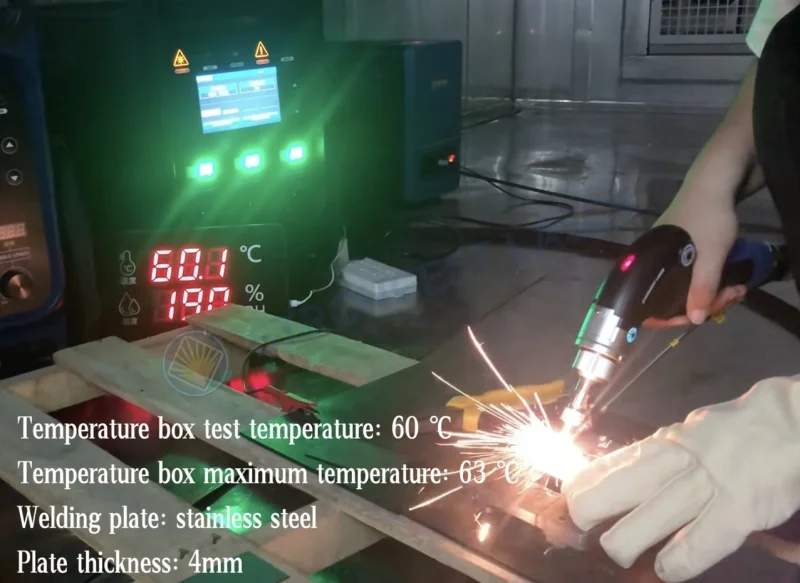
Medical Device Manufacturing: Laser welding is essential in the medical field for creating sterile, high-precision welds for surgical tools, implants, and other medical devices. Materials such as stainless steel and titanium can be welded with minimal thermal impact, crucial for medical-grade components.
Home Appliance Industry: In home appliance manufacturing, handheld laser welders are used to join or repair components like stainless steel sinks, frames, and internal parts. They ensure strong, clean welds without post-weld processing, enhancing the production quality and lifespan of appliances.

Challenges and Considerations in Industrial Use
While highly effective, handheld laser welding machines come with their own set of considerations:
Material Limitations: Handheld laser welders are highly effective for thin and medium materials but may struggle with thicker metals that require higher energy input.
Power Supply and Energy Requirements: Although relatively efficient, laser welders need stable power sources, which can sometimes limit field use.
Operator Training and Safety: Operators need adequate training to manage laser safety, as improper use can lead to eye and skin hazards. While user-friendly, these machines require a solid understanding of laser handling protocols.
Initial Investment and Maintenance: Handheld laser welders can represent a significant investment, though their durability and lower maintenance often offset initial costs in the long run.
Future Trends and Technological Advancements
Handheld laser welding technology is continually evolving, with improvements in laser source technology leading to more powerful, efficient, and user-friendly machines. Newer lasers offer even higher precision, broader material compatibility, and energy efficiency, expanding their appeal across industries. Integration with automation is also gaining traction, with robots increasingly working alongside laser welders to improve consistency, especially in high-volume manufacturing.
In emerging fields, such as renewable energy and electric vehicle production, handheld laser welders are finding a niche due to their compatibility with lightweight materials and their adaptability in working with battery components and other specialized parts.
Conclusion
Handheld laser welding machines represent a significant advancement in welding technology, offering precision, portability, and versatility across a wide range of industries. From automotive and aerospace to electronics and medical devices, their role is integral to enhancing production efficiency and quality. As technology advances and more industries adopt laser welding, the potential applications of handheld laser welders are poised to expand, further solidifying their place as a transformative tool in modern manufacturing. With their adaptability and efficiency, handheld laser welding machines are reshaping how industries approach precision welding tasks, driving innovation and setting new standards for weld quality and productivity.
STRONGEST LASER, an expert in the field of laser welding, with high-power fiber laser technology as the core, has always been committed to the research and development and equipment production in the application fields of conventional laser welding, special laser hybrid welding, etc. Our STR-HW series handheld welding machine provides customers with high-efficiency, high-melting depth, high-energy-saving, high-convenience, and high-stability welding experience, which can meet the metal welding needs of various materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, galvanized sheet, brass, etc.









