In modern metal fabrication, welding thin plates presents one of the toughest challenges. Materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel plates with reduced thickness are widely used in automotive, electronics, furniture, and precision equipment manufacturing. However, welding them without distortion, burn-through, or loss of aesthetic appeal is a delicate process.
Traditional methods such as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding often struggle with thin plates. Excess heat input can warp the material, leave uneven seams, or require extensive post-processing to achieve the desired finish.
This is where handheld laser welders have revolutionized the field. With their ability to deliver highly concentrated energy with pinpoint accuracy, they provide unmatched precision in thin plate welding. This article explores the unique challenges of thin plate welding, how handheld laser welders solve them, their key advantages, applications, best practices, and what the future holds.
Challenges in Thin Plate Welding
Welding thin plates requires a high level of control and consistency. Some of the common challenges include:
Low Heat Tolerance
Thin plates dissipate heat quickly, but at the same time, they are very susceptible to localized overheating. Too much energy causes warping or burn-through, making it difficult to maintain dimensional accuracy.
Maintaining Joint Strength
For thin plates, joint integrity is vital. Conventional welding may fail to achieve the necessary penetration without compromising the structure, leading to weak spots or cracks.
Aesthetic Requirements
Thin plates are often visible in the final product, such as in furniture, consumer electronics, or vehicle panels. Any distortion, rough weld seams, or discoloration can compromise visual appeal and reduce product value.
Balancing Speed and Accuracy
Manufacturers often need high-speed production without sacrificing quality. Conventional processes can be slow and require rework, increasing overall costs and cycle times.
How Handheld Laser Welders Address These Challenges
Handheld laser welding machines provide solutions by combining energy efficiency with precise heat control. Here’s how they overcome thin plate welding issues:
High Precision Heat Control
Laser welding directs energy in a concentrated beam to a specific spot, limiting heat spread. This reduces thermal distortion and allows clean welds even on ultra-thin materials.
Narrow Weld Seams
The beam produces extremely fine weld seams, often less than 0.5 mm wide. This precision makes it ideal for thin plates where wide seams would look unattractive or structurally weaken the material.
Adjustable Power Settings
Modern handheld laser welders let operators tailor power, pulse, and beam parameters to match the material and thickness. This flexibility ensures the right penetration depth without excess heat input.
Minimal Filler Requirement
Unlike traditional welding, laser welding often eliminates or reduces the need for filler material, cutting costs and simplifying operations.

Key Advantages in Thin Plate Applications
Reduced Deformation
Since the laser introduces limited heat into the material, distortion and warping are greatly minimized. This is particularly important for precision industries where dimensional accuracy matters.
Superior Seam Quality
Handheld laser welders produce smooth, uniform seams that are visually appealing. In many cases, no post-weld grinding, polishing, or sanding is necessary, saving time and labor.
High Welding Speed
Laser welders can achieve speeds 2–10 times faster than TIG welding while maintaining or even improving quality. This accelerates production and improves throughput in thin plate applications.
Material Versatility
They are effective with stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, titanium, and various alloys. Thin plates across multiple industries benefit from this versatility.
Lower Overall Costs
Reduced rework, lower filler usage, and faster cycle times result in significant cost savings for manufacturers.
Practical Applications of Handheld Laser Welding in Thin Plates
The benefits of handheld laser welding extend across multiple industries:
Automotive Manufacturing
Body panels, fuel tanks, brackets, and exhaust components often use thin sheet metal. Laser welding ensures precision and reduces cosmetic defects in visible areas.
Electronics and Appliances
Thin stainless steel housings, aluminum casings, and lightweight frames require clean welds with no warping. Handheld laser welders achieve this with minimal rework.
Furniture and Interior Design
Thin stainless steel frames and decorative elements demand smooth seams and high aesthetics. Laser welding provides flawless joints without excessive heat marks.
Medical and Precision Equipment
Thin casings for medical instruments and fine mechanical parts rely on distortion-free welding to maintain accuracy and sterility.
Aerospace and Lightweight Structures
Thin aluminum sheets and alloys are crucial in lightweight designs. Laser welding enables strong, accurate joints that meet safety standards.
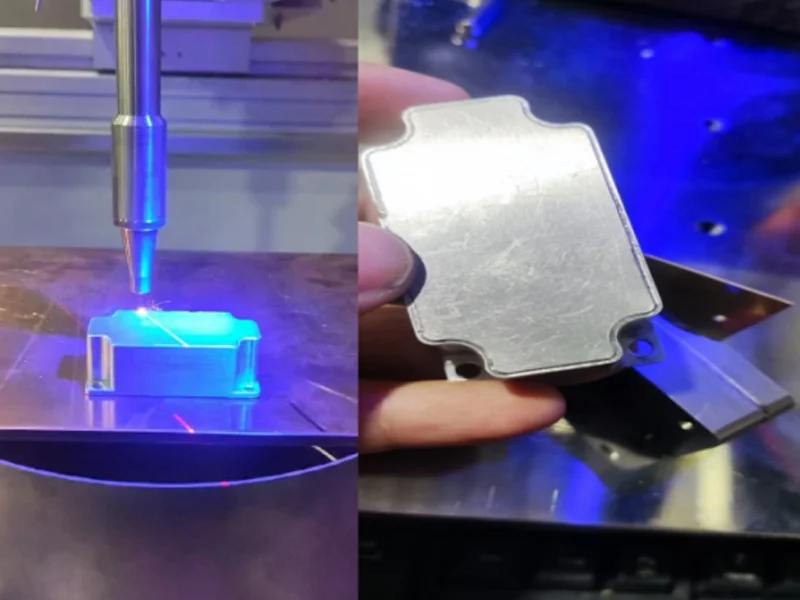
Best Practices for Thin Plate Laser Welding
To maximize the benefits of handheld laser welders in thin plate applications, operators should follow these best practices:
Choose Proper Power and Settings
Match laser power and pulse frequency to the specific material thickness. Lower settings are often best for ultra-thin plates to prevent burn-through.
Maintain Accurate Beam Focus
Keeping the beam precisely focused ensures consistent penetration and seam quality. A small deviation can lead to poor welds or weak spots.
Ensure Tight Joint Fit-Up
Thin plates require minimal gaps at the joint for seamless welding. Proper preparation before welding is key.
Operator Training
Though handheld laser welders are user-friendly, training helps operators maintain consistent weld speeds, hand stability, and quality results.
Protective Environment
Using shielding gas such as argon enhances weld quality and prevents oxidation, especially for stainless steel and aluminum plates.
Future of Handheld Laser Welding in Thin Plate Fabrication
As industries continue to shift toward lighter, thinner, and more precise designs, handheld laser welding is expected to play an even greater role. Key trends include:
Increased Adoption
Sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics are steadily transitioning from TIG welding to laser welding for thin plate components.
Integration with Automation
Future models may integrate AI-driven controls, robotic assistance, or smart sensors to ensure even higher consistency and precision.
Cost Reduction
As the technology matures and scales, handheld laser welders are becoming more affordable, making them accessible to medium and small-scale manufacturers.
Sustainability Benefits
With reduced energy consumption, minimal waste, and cleaner seams, handheld laser welding supports environmentally friendly manufacturing practices.
Conclusion
Thin plate welding demands precision, consistency, and visual perfection. Traditional welding techniques often struggle to deliver these results, leading to defects, distortions, and inefficiencies. Handheld laser welders overcome these challenges by offering pinpoint heat control, high-quality seams, faster speeds, and versatility across a wide range of materials.
For manufacturers in automotive, electronics, furniture, aerospace, and precision industries, handheld laser welding has emerged as the preferred solution for thin plate applications. As technology advances, its role will only grow stronger in shaping the future of modern fabrication.
At Strion laser, we are committed to providing cutting-edge handheld laser welding solutions that ensure unmatched precision, efficiency, and quality in thin plate welding.














