STRION LASER has achieved a groundbreaking advancement in dissimilar material welding technology, specifically targeting the long-standing challenges of joining copper (Cu) and aluminum (Al)—a critical combination for industries like electric vehicle (EV) battery manufacturing, aerospace, and electronics.
This article details STRION LASER’s solutions, backed by experimental data (Tables 1–2), and demonstrates their industrial applicability in achieving >30% stronger joints and near-parent-material conductivity.
| Characteristic | Cu | Al | Effect of differences on welding |
| Melting point | 1083℃ | 660℃ | When copper is melted, aluminum is prone to overheating and vaporization, resulting in an uneven molten pool |
| Thermal conductivity | 401 W/m·K(@20℃) | 237 W/m·K(@20℃) | Copper dissipates heat quickly and requires a higher energy input to melt, which can easily lead to excessive melting of aluminum |
| Laser absorbance (infrared) | <20%(@1064nm) | ~60%(@1064nm) | Copper has high reflectivity to infrared light and low energy utilization |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | 16.5×10⁻⁶/℃(@20℃) | 23.6×10⁻⁶/℃(@20℃) | The shrinkage difference during cooling is large, and the joint is prone to stress cracking |
| Intermetallic compounds | Result in crispy phase CuAl₂、Cu₉Al₄ | —— | When the thickness of the compound layer exceeds 5 μm, the joint toughness decreases significantly |
Table.1 Difficulties due to material characteristics
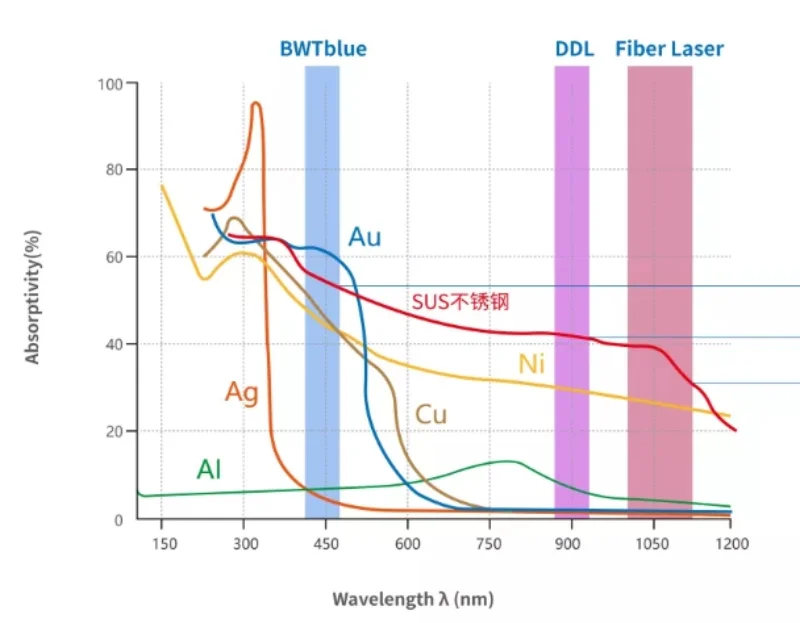
Table.2 Absorption rate of different materials
Surface pretreatment technology
Copper surface texturing: laser etching forms micron-level grooves (depth 5~10μm), which increases the wetting area of molten aluminum and increases the bonding strength by 30%.
Copper plating on aluminum surface: A 5~10μm copper layer is formed on the surface of aluminum by electroplating or electroless plating to alleviate the violent reaction caused by direct contact between copper and aluminum.
Wavelength selection
Blue laser (450nm): high copper absorption, suitable for copper and aluminum sheet welding with a thickness of ≤2mm (such as battery tabs).
Green laser (532nm): compromise copper-aluminum absorption, suitable for medium-thickness (2~5mm) welding.
Composite laser (blue light + infrared light): blue light heats copper, infrared light heats aluminum, and synchronous melting is realized.
The middle layer introduces technology
Nano coating: The graphene nanolayer (thickness < 10nm) is coated on the copper surface, which can inhibit the diffusion of copper atoms and increase the laser absorption rate by 15%~20%.
STRION LASER’s breakthrough in copper-aluminum dissimilar welding sets a new benchmark for precision and reliability in multi-material joining.
As industries increasingly demand lightweight, high-conductivity hybrids (e.g., Cu-Al busbars in EVs), STRION LASER’s technology paves the way for mass production with repeatable quality. Future R&D will focus on real-time monitoring systems and AI-driven parameter optimization to further refine weld integrity.