1.Introduction
Hybrid laser welding, a technology that combines laser welding and traditional arc welding, has revolutionized the welding industry by offering a blend of the precision of laser welding and the versatility of arc welding. This method involves the simultaneous use of a high-powered laser beam and an electric arc, which together provide significant advantages in welding efficiency, quality, and material handling. As industries strive for faster, more precise, and cost-effective welding solutions, hybrid laser welding has become increasingly important in modern manufacturing.
The technology has found applications across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, and heavy industries, where precision, speed, and the ability to handle thicker materials are crucial. Hybrid laser welding has opened up new possibilities for manufacturers to produce high-quality welds while reducing production times and costs.

2. Overview of Laser Hybrid Welding Technology
2.1 Definition and Working Principle of Laser Hybrid Welding
Laser hybrid welding refers to a welding process where laser welding and arc welding techniques are combined in a single operation. The laser provides concentrated heat to the workpiece, while the arc ensures deeper penetration and stable arc characteristics. The simultaneous use of both processes allows for high-speed welding with improved weld quality. The laser melts the material’s surface, while the arc deepens the weld, ensuring a more robust bond between the materials.
2.2 Comparison of Laser Hybrid Welding with Traditional Welding Methods
Traditional welding methods such as Metal Inert Gas (MIG) and Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding rely on heat generated from an electric arc to melt the materials. In contrast, hybrid laser welding offers several advantages:
- Speed: Laser hybrid welding is faster than traditional welding due to the high heat intensity of the laser, which can melt material quickly.
- Precision: The laser provides a high level of control over the welding process, allowing for more precise welds.
- Penetration: The combination of laser and arc results in deeper penetration, making it possible to weld thicker materials than MIG or TIG welding.
2.3 Equipment Composition and Key Technologies of Laser Hybrid Welding
The equipment used in laser hybrid welding typically includes:
- Laser Source: A high-powered laser beam is directed onto the weld area.
- Arc Source: An arc welding power supply (such as MIG or TIG) is used to create a welding arc alongside the laser.
- Control System: A computerized system that controls both the laser and arc welding parameters in real-time to ensure optimal welding conditions.
- Nozzle and Welding Torch: The nozzle directs the laser beam and arc at the workpiece and maintains the proper distance and angle.
3. STRONGEST LASER’s Laser Hybrid Welding
STRONGEST LASER offers advanced laser hybrid welding solutions that combine the advantages of both laser welding and arc welding. Our technology is particularly mature in industries such as shipbuilding, automobile production, and rail vehicle manufacturing.
3.1 Red and Blue Laser Hybrid Welding
STRONGEST LASER’s red and blue laser hybrid welding system offers enhanced flexibility, providing better energy concentration and improved heat control. The red laser provides high power density for precision, while the blue laser enhances material absorption and weld depth.
3.2 Laser-MIG Hybrid Welding
STRONGEST LASER’s laser-MIG hybrid welding is an effective solution for thick material welding, as it combines the rapid speed and precision of laser welding with the deep penetration capability of MIG welding. This configuration is especially useful for high-strength materials and large-scale manufacturing.
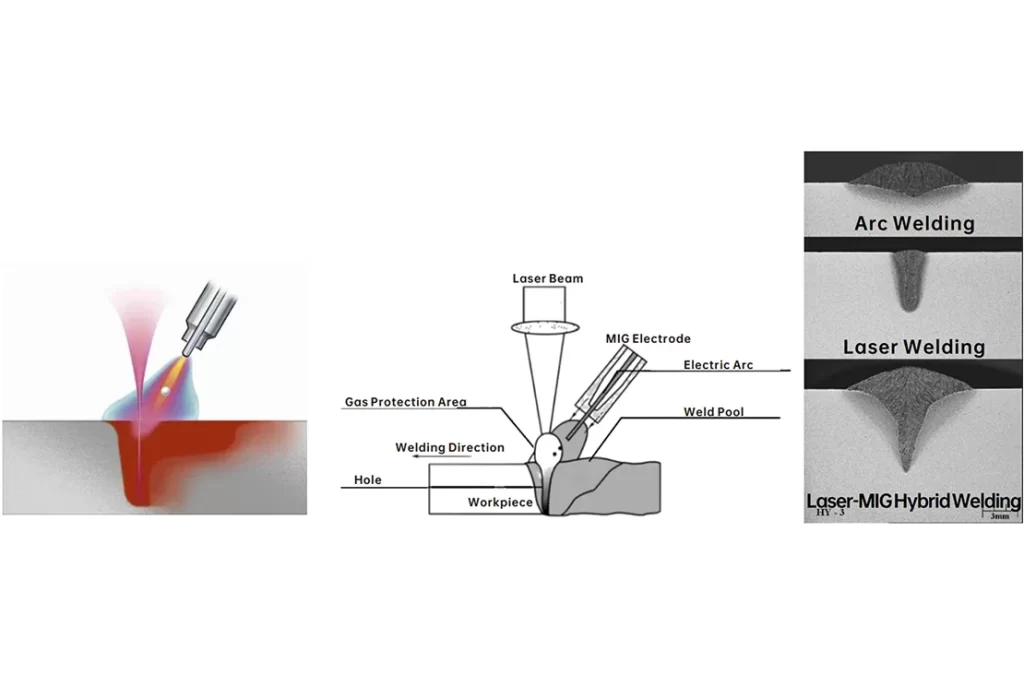
3.3 What’s the hybrid welding process?
The hybrid welding process is an advanced welding technique that combines laser welding and arc welding to achieve high efficiency and superior weld quality. By merging these two processes, hybrid welding overcomes the limitations of traditional methods and is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and shipbuilding industries.
Step 1: Preparation
Before starting the hybrid welding process:
Material Selection – Choose compatible metals such as steel, aluminum, or titanium.
Joint Design – Ensure proper alignment and gap tolerance.
Surface Cleaning – Remove rust, oil, or debris to prevent weld defects.
Step 2: Setting Up the Welding System
Hybrid welding requires precise equipment setup:
Laser Source – Provides a concentrated heat beam for deep penetration.
Arc Welding Equipment – Supplies additional heat and filler material for stronger joints.
Synchronization – Align both heat sources for optimal energy distribution.
Step 3: Welding Process
During welding:
The laser beam penetrates the material quickly, creating a narrow and deep weld.
The arc welding component adds filler metal and stabilizes the molten pool.
Continuous monitoring ensures defect-free, high-strength welds.
Step 4: Post-Weld Treatment
After welding:
Inspection – Check for porosity, cracks, or misalignment.
Finishing – Minimal grinding or polishing is needed due to precise heat control.
4. Advantages of Hybrid Laser Welding
4.1 Improve Welding Quality
One of the key benefits of hybrid laser welding is the ability to produce high-quality welds. The low heat-affected zone (HAZ) reduces the risk of warping, cracking, and residual stresses in the welded materials. The strength and durability of the welded joint are also enhanced, making the process ideal for critical applications in automotive, aerospace, and heavy industries.
4.2 Improve Welding Efficiency
Hybrid laser welding enables high-speed, continuous welding, resulting in increased productivity. The ability to weld materials quickly and precisely leads to shorter production cycles, reducing the time required to complete welds. Additionally, this technology allows manufacturers to handle thicker materials, expanding the range of applications.
4.3 Reduce Heat Input
Compared to traditional welding methods, hybrid laser welding requires lower heat input, which reduces the risk of material distortion and warping. This lower heat input also results in less heat penetration, which is crucial when working with heat-sensitive materials.
4.4 Good Welding Stability
The hybrid process provides excellent welding stability due to the precision control of both the laser and the arc. The laser energy is concentrated, which ensures a stable welding process even when working with high-strength or difficult-to-weld materials.
4.5 Applicable to a Variety of Materials
Hybrid laser welding is suitable for a broad range of materials, including high-strength steels, aluminum alloys, and other non-ferrous metals. The ability to weld different types of materials with precision makes this technology highly versatile in various industries.
5. Disadvantages of Hybrid Laser Welding
5.1 High Equipment Cost
One of the major drawbacks of hybrid laser welding is the high initial cost of the equipment. Laser welding systems are expensive, which can be a barrier for smaller companies or those just entering the manufacturing industry. The cost of the laser source, combined with the need for specialized equipment and a skilled workforce, can make hybrid laser welding a significant financial investment.
5.2 High Technical Requirements
The operation of hybrid laser welding equipment requires highly skilled technicians who are capable of setting up, operating, and maintaining the systems. The complexity of combining laser and arc welding technology increases the technical requirements, necessitating advanced training and expertise.
5.3 High Requirements for Materials and Surfaces
For optimal results, materials need to be clean and free from contaminants. Surface preparation is particularly important when welding materials like aluminum, which is prone to oxidation. The presence of oxide layers can interfere with the weld quality, making it more challenging to achieve a strong and stable bond.
5.4 Welding Depth Limit
While hybrid laser welding can handle thicker materials than traditional welding methods, the depth and stability of the weld may be limited outside certain thickness ranges. For very thick materials, other welding methods might be more suitable for achieving the required weld strength.
6. Application Areas of Hybrid Laser Welding
Hybrid laser welding is being used in a variety of industries where the need for precision and speed is paramount, and leading laser welding machine manufacturer like strion laser continue to advance this technology to meet the growing demands of modern industrial applications.
- Automobile Manufacturing: Laser hybrid welding for automotive manufacturing is widely applied in car body welding, frame construction, and component assembly, where high-quality, strong, and repeatable welds are essential for structural integrity and production efficiency.
- Aerospace: This technology is employed for welding aircraft structural parts and critical components, where both precision and durability are critical.
- Electronics Industry: Hybrid laser welding is used for high-precision welds in the production of electronic components and devices.
- Steel and Heavy Industry: The ability to weld thick materials efficiently makes hybrid laser welding ideal for heavy industries, with the hybrid laser welding system for shipbuilding playing a key role in hull fabrication, structural welding, and large steel component assembly.
- Other Applications: Hybrid laser welding is also used in rail vehicle manufacturing, medical equipment, and other specialized sectors requiring strong, precise welds.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, hybrid laser welding offers significant advantages in terms of welding quality, speed, and material versatility. Its ability to handle thicker materials, reduce heat input, and improve welding efficiency makes it an essential tool in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing. However, the high initial cost of equipment, technical complexity, and material requirements are some of the challenges that need to be addressed. As technology advances, hybrid laser welding is expected to evolve further, with improvements in affordability and ease of use, making it an even more attractive option for modern manufacturing processes. The future of hybrid laser welding is promising, and continued research and development will undoubtedly enhance its capabilities and broaden its applications.